Electric Vehicle Facts
They have four wheels, a steering wheel and a gas pedal... but the mechanics of an EV are much simpler than gas-powered motors. Here's a look at the key systems that most electric vehicles utilize.
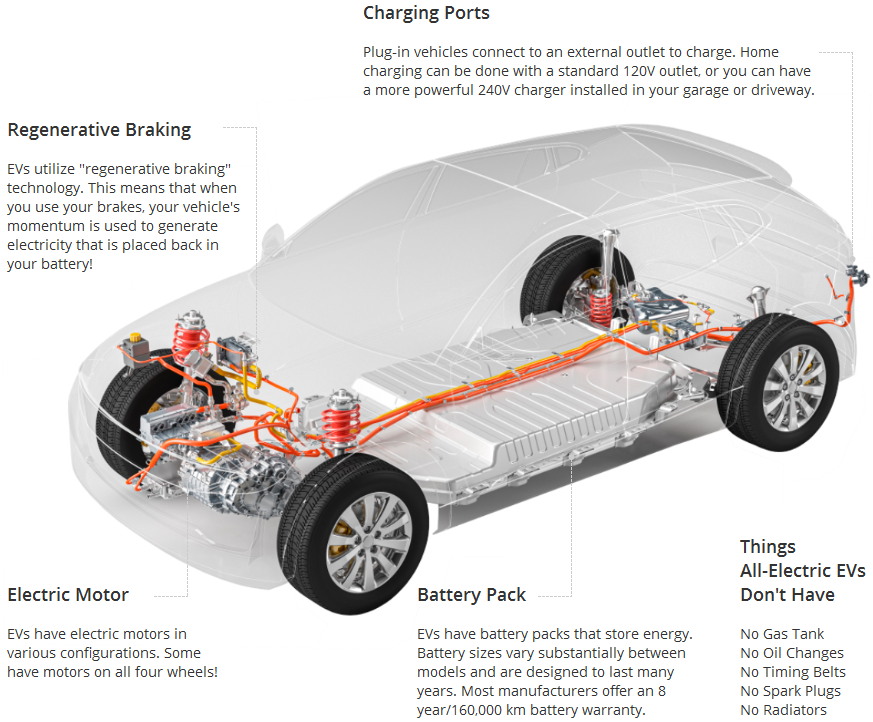

Charging your EV requires plugging into a charger connected to the electric grid, also called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). There are three major categories of chargers, based on the amount of power the charger can provide:
AC Level 1
Provides charging through a 120V AC plug and does not require installation of additional charging equipment. Level 1 can typically deliver 3 to 8 km of range per hour of charging. Level 1 is most often used in home applications, but is sometimes used at workplaces. A full charge may take up to 24 hours with Level 1 120V charging.
AC Level 2
Provides charging through a 240V plug and requires the installation of additional charging equipment by a qualified electrician/installer. Level 2 chargers typically deliver 15 to 30 km of range per hour of charging. Level 2 is used in homes, workplaces and for some public charging. Level 2 charging systems provide slight energy efficiency benefits over Level 1 chargers - savings estimates vary based on length of charge time.
View level 2 home chargers
DC Fast-Charge
Provides charging through 480V AC input and requires specialized, high-powered charging equipment and special equipment in the vehicle itself. DC Fast-Charging can deliver an 80 percent battery charge or 100 to 160 km of range for most EV models in about 20 to 30 minutes of charging. This format is used in public charging stations, especially along heavy-traffic corridors. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles typically do not have fast charging capabilities.
Find public chargers
Electric vehicle batteries are typically designed to last for the expected life of the vehicle, but battery life should be considered when calculating the extended cost of ownership, as all batteries eventually wear out and must be replaced. Battery replacement is typically costly, but keep in mind that gas powered vehicle equipment, such as motors and transmissions, have a lifespan too. The rate at which batteries expire depends on the type of battery and how they are used.
The failure rate of some electric vehicles batteries already on the road is as low as 0.003 percent2. There are also high mileage warranties on electric vehicle batteries available with many manufacturers. Review manufacturer information carefully when selecting an EV model.
Emissions
EVs produce no tailpipe emissions. Even when the power is generated using fossil fuels, electric vehicles usually show significant reductions in overall global carbon emissions over gasoline vehicles due to the highly carbon-intensive process of mining, pumping, refining and transporting gasoline.
Energy Efficiency
Internal combustion engines are relatively inefficient at converting fuel energy to propulsion as most of the energy is wasted as heat. Electric motors are more efficient in converting stored energy into propulsion, and electric-drive vehicles do not consume energy while at rest or coasting. Regenerative breaking can be used to re-capture energy during braking that is stored back in the battery. Typically, conventional gasoline engines effectively use only 15 percent of the fuel-energy content to move the vehicle or to power accessories, while electric-drive vehicles have on-board efficiency of around 80 percent3.
Electric cars are not completely environmentally friendly as there can be significant issues to consider related to energy and material use in the manufacturing process. This may include energy-intensive manufacturing processes or the mining and refinement of chemicals and materials.
Estimate carbon reduction
The average Canadian household spends nearly one-fifth of its total family expenditures on transportation, thus saving on fuel can make a big difference in the average family's budget4. Electricity is less expensive than gasoline and EVs are more efficient than gas-powered vehicles. Electricity prices are also generally much more stable than gasoline prices.
Estimate fuel savings
Battery Electric Vehicles (or BEV) require less maintenance than conventional vehicles because there are fewer fluids (like oil and transmission fluid) to change, and far fewer moving parts. EVs require minimal scheduled maintenance to their electrical systems, which can include the battery, electrical motor, and associated electronics. Because of regenerative braking, brake systems on EVs typically last longer than on conventional vehicles.
No Oil Changes: BEVs do not require engine oil, thus there are no oil changes (normally required every 5,000 to 11,000 km; requirements vary by automobile manufacturer).
No Spark Plugs and Wires: BEVs do not require spark plugs and wires, thus no replacements (estimated replacement at approximately160,000 kilometers on gas engine).
No Exhaust System: BEVs do not have mufflers or catalytic converters, two components of your exhaust system that can fail and result in expensive replacements.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) have an electric motor and a gas motor. Cars with gas motors still require the standard maintenance a regular gas-powered vehicle requires (oil changes, spark plugs and wires, exhaust systems, etc.), but at less-frequent intervals.
Sources
1 U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the Omnibus Household Survey.
2 U.S. Department of Energy – Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Alternative Fuels Data Center, Maintenance and Safety of Hybrid and Plug-In Electric Vehicles.
3 Shah, Saurin D. (2009), Plug-In Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington? (1st edition). The Brookings Institution. pp. 29, 37 and 43.
4 Statistics Canada: Survey of Household Spending, 2019.

Charging your EV

Charging your EV requires plugging into a charger connected to the electric grid, also called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). There are three major categories of chargers, based on the amount of power the charger can provide:
AC Level 1
Provides charging through a 120V AC plug and does not require installation of additional charging equipment. Level 1 can typically deliver 3 to 8 km of range per hour of charging. Level 1 is most often used in home applications, but is sometimes used at workplaces. A full charge may take up to 24 hours with Level 1 120V charging.
AC Level 2
Provides charging through a 240V plug and requires the installation of additional charging equipment by a qualified electrician/installer. Level 2 chargers typically deliver 15 to 30 km of range per hour of charging. Level 2 is used in homes, workplaces and for some public charging. Level 2 charging systems provide slight energy efficiency benefits over Level 1 chargers - savings estimates vary based on length of charge time.
View level 2 home chargers
DC Fast-Charge
Provides charging through 480V AC input and requires specialized, high-powered charging equipment and special equipment in the vehicle itself. DC Fast-Charging can deliver an 80 percent battery charge or 100 to 160 km of range for most EV models in about 20 to 30 minutes of charging. This format is used in public charging stations, especially along heavy-traffic corridors. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles typically do not have fast charging capabilities.
Find public chargers
 EV Battery Information
EV Battery Information
Electric vehicle batteries are typically designed to last for the expected life of the vehicle, but battery life should be considered when calculating the extended cost of ownership, as all batteries eventually wear out and must be replaced. Battery replacement is typically costly, but keep in mind that gas powered vehicle equipment, such as motors and transmissions, have a lifespan too. The rate at which batteries expire depends on the type of battery and how they are used.
The failure rate of some electric vehicles batteries already on the road is as low as 0.003 percent2. There are also high mileage warranties on electric vehicle batteries available with many manufacturers. Review manufacturer information carefully when selecting an EV model.
 Emissions & energy efficiency
Emissions & energy efficiency
EmissionsEVs produce no tailpipe emissions. Even when the power is generated using fossil fuels, electric vehicles usually show significant reductions in overall global carbon emissions over gasoline vehicles due to the highly carbon-intensive process of mining, pumping, refining and transporting gasoline.
Energy Efficiency
Internal combustion engines are relatively inefficient at converting fuel energy to propulsion as most of the energy is wasted as heat. Electric motors are more efficient in converting stored energy into propulsion, and electric-drive vehicles do not consume energy while at rest or coasting. Regenerative breaking can be used to re-capture energy during braking that is stored back in the battery. Typically, conventional gasoline engines effectively use only 15 percent of the fuel-energy content to move the vehicle or to power accessories, while electric-drive vehicles have on-board efficiency of around 80 percent3.
Electric cars are not completely environmentally friendly as there can be significant issues to consider related to energy and material use in the manufacturing process. This may include energy-intensive manufacturing processes or the mining and refinement of chemicals and materials.
Estimate carbon reduction
 Reduced Operating Costs
Reduced Operating Costs
The average Canadian household spends nearly one-fifth of its total family expenditures on transportation, thus saving on fuel can make a big difference in the average family's budget4. Electricity is less expensive than gasoline and EVs are more efficient than gas-powered vehicles. Electricity prices are also generally much more stable than gasoline prices.
Estimate fuel savings
 Reduced Maintenance Requirements
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
Battery Electric Vehicles (or BEV) require less maintenance than conventional vehicles because there are fewer fluids (like oil and transmission fluid) to change, and far fewer moving parts. EVs require minimal scheduled maintenance to their electrical systems, which can include the battery, electrical motor, and associated electronics. Because of regenerative braking, brake systems on EVs typically last longer than on conventional vehicles. No Oil Changes: BEVs do not require engine oil, thus there are no oil changes (normally required every 5,000 to 11,000 km; requirements vary by automobile manufacturer).
No Spark Plugs and Wires: BEVs do not require spark plugs and wires, thus no replacements (estimated replacement at approximately160,000 kilometers on gas engine).
No Exhaust System: BEVs do not have mufflers or catalytic converters, two components of your exhaust system that can fail and result in expensive replacements.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) have an electric motor and a gas motor. Cars with gas motors still require the standard maintenance a regular gas-powered vehicle requires (oil changes, spark plugs and wires, exhaust systems, etc.), but at less-frequent intervals.
Sources
1 U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the Omnibus Household Survey.
2 U.S. Department of Energy – Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Alternative Fuels Data Center, Maintenance and Safety of Hybrid and Plug-In Electric Vehicles.
3 Shah, Saurin D. (2009), Plug-In Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington? (1st edition). The Brookings Institution. pp. 29, 37 and 43.
4 Statistics Canada: Survey of Household Spending, 2019.
